Creating API Collections
Learn how to organize and manage your API endpoints using collections in Maeris. Keep your APIs structured, easy to navigate, and ready for testing.
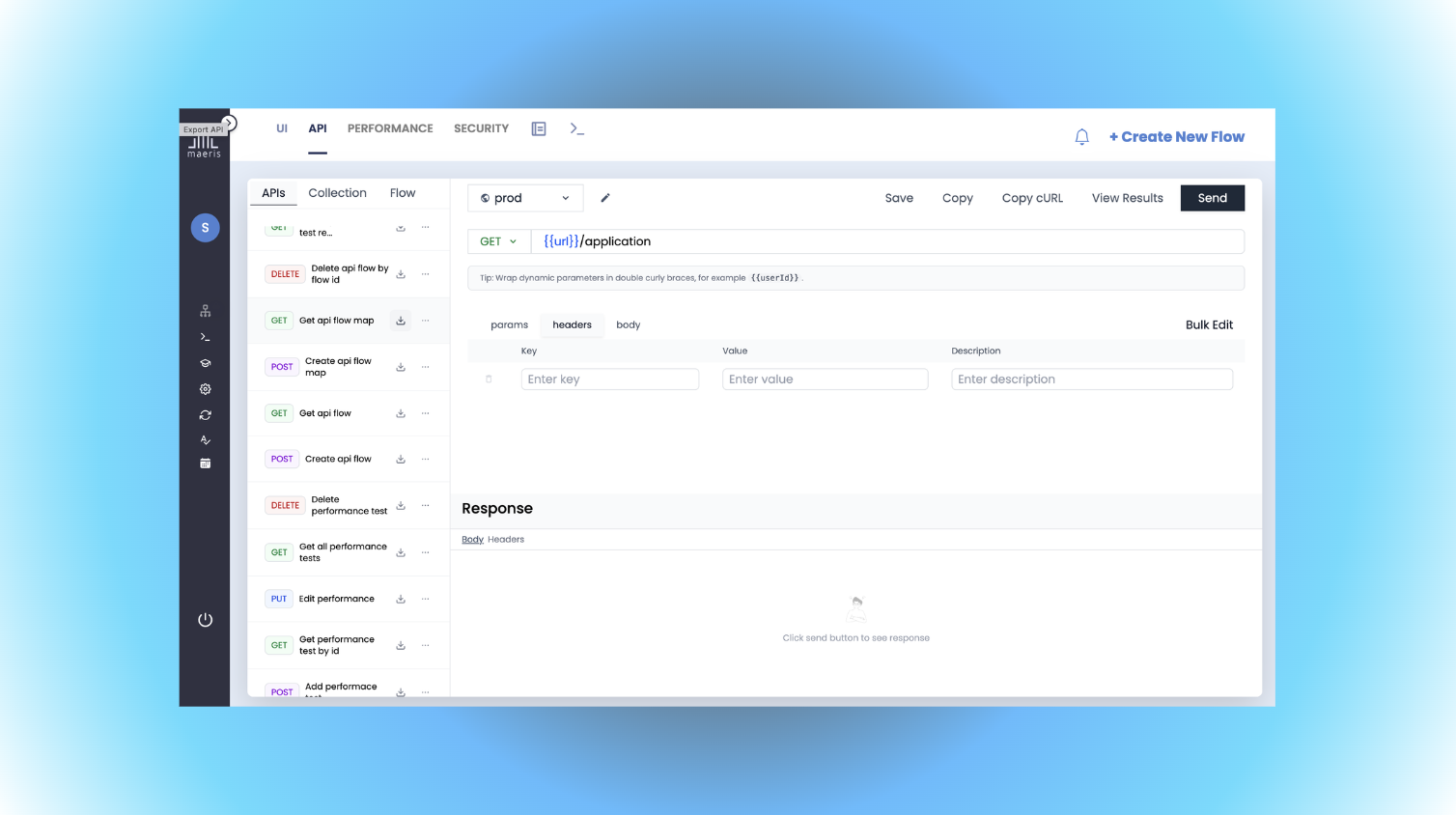
What are API Collections?
API Collections are organized groups of API endpoints that help you structure your API testing. Think of them as folders that contain related API requests, making it easy to:
- Organize endpoints by feature, module, or service
- Group related API calls together logically
- Share collections with team members
- Maintain a clear overview of your API landscape
- Reuse requests across different test scenarios
Creating Your First Collection
Follow these steps to create a new API collection:
- Navigate to API Testing: Go to the API Testing section in Maeris
- Click "New Collection": Find and click the "New Collection" button (usually in the top-right corner)
- Name Your Collection: Give it a descriptive name (e.g., "User Management APIs" or "Payment Service")
- Add Description (Optional): Add a brief description to help team members understand the collection's purpose
- Save: Click "Create" or "Save" to create your collection
Adding API Requests to a Collection
Once you have a collection, you can add API requests to it:
- Open Your Collection: Click on the collection you want to add requests to
- Click "Add Request": Find the "Add Request" or "New Request" button
- Configure the Request:
- Select HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH)
- Enter the endpoint URL
- Add headers if needed
- Include request body for POST/PUT requests
- Name Your Request: Give it a clear, descriptive name (e.g., "Get User by ID")
- Save: Save the request to your collection
Organizing Collections
Good organization makes your API testing more efficient. Here are some strategies:
Organize by Feature
Group APIs by application features:
- User Management
- Authentication
- Payment Processing
- Product Catalog
Organize by Service
If you have a microservices architecture:
- User Service APIs
- Order Service APIs
- Notification Service APIs
Organize by Environment
Separate collections for different environments:
- Development APIs
- Staging APIs
- Production APIs
Configuring API Requests
Each API request in your collection can be configured with:
Basic Configuration
- Method: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, etc.
- URL: The endpoint URL (can include variables)
- Description: What this request does
Headers
- Authorization headers (Bearer tokens, API keys)
- Content-Type
- Custom headers your API requires
Query Parameters
- URL query parameters
- Filtering and pagination parameters
Request Body
- JSON payloads for POST/PUT requests
- Form data
- Raw text or XML
Using Variables in Collections
Variables make your collections more flexible and reusable:
- Base URL Variables: Set your API base URL once and reuse it across all requests
- Authentication Tokens: Store and reuse authentication tokens
- Dynamic Values: Use variables for IDs, timestamps, or other dynamic values
- Environment-Specific Values: Switch between dev, staging, and production easily
Example: Use {{baseUrl}}/users instead of hardcoding the full URL
Testing API Requests
Once you've added requests to your collection, you can test them:
- Select a Request: Click on the request you want to test
- Click "Send" or "Run": Execute the request
- View Response: See the response status, headers, and body
- Check Response Time: View how long the request took
- Review Headers: Inspect response headers for debugging
Sharing Collections
Collections can be shared with your team:
- Team Access: Share collections with team members for collaboration
- Export: Export collections as JSON files to share or backup
- Import: Import collections from files or other team members
- Version Control: Keep track of changes and maintain version history
Best Practices
- Use Descriptive Names: Name collections and requests clearly so their purpose is obvious
- Add Documentation: Include descriptions for collections and requests to help your team
- Organize Logically: Structure collections in a way that makes sense for your team and product
- Use Variables: Avoid hardcoding URLs, tokens, and other values - use variables instead
- Version Your Collections: Keep track of changes as your APIs evolve
- Test Regularly: Run requests frequently to catch API changes early
Next Steps
Now that you know how to create API collections:
- Learn about building API flows to chain requests together
- Explore adding assertions and validations to your requests
- Check out performance testing to test your APIs under load